1. What Is Cardiac Screening?
Cardiac screening involves a series of tests designed to detect heart conditions before symptoms appear. These tests evaluate your heart’s function and the health of your blood vessels, helping to catch potential issues early, when they are most treatable.
2. Who Should Consider Screening?
You may benefit from cardiac screening if any of the following apply:
Family history of early heart disease
Known risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, sedentary lifestyle
Age–related risk, particularly if you're over 40
Athletes, especially in endurance sports, as intense activity can unmask underlying conditions
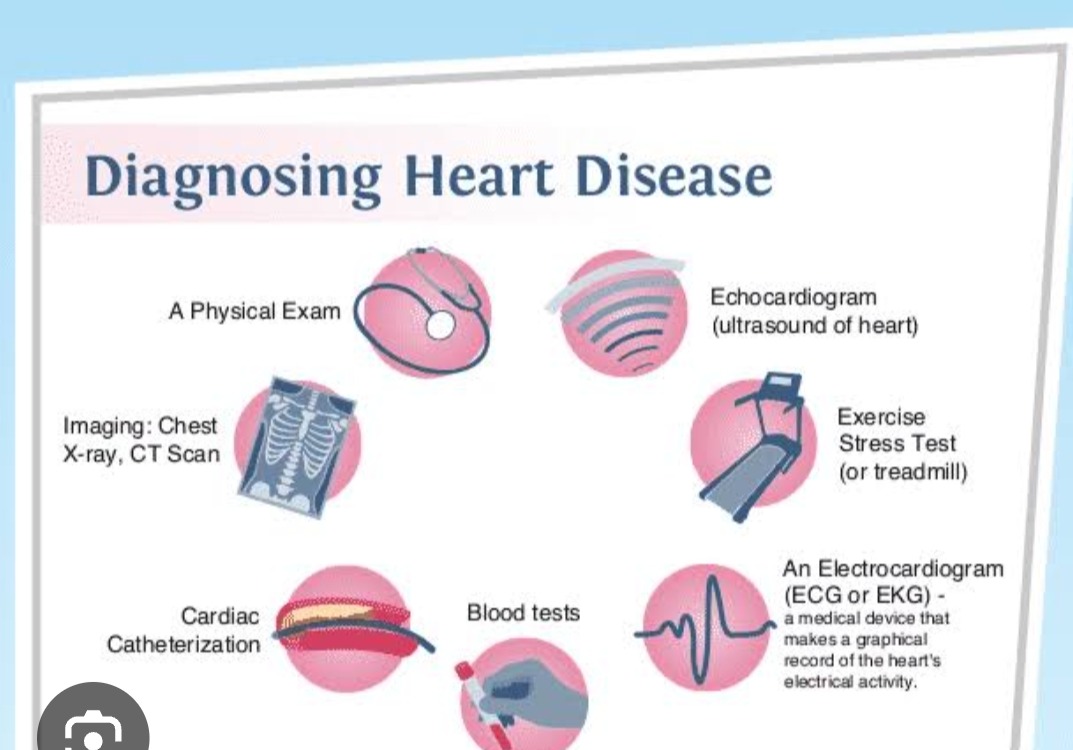
3. Screening Tests Explained
Test What It Does What to Expect
Blood Tests Measure cholesterol, blood glucose, inflammation markers (e.g., hs‑CRP)
Typically requires fasting for several hours beforehand
Blood Pressure Check Evaluates your heart’s workload and arterial health
Quick and painless, often part of routine checks
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Records the heart’s electrical activity to detect rhythm issues
Painless, electrodes placed on chest/limbs
Echocardiogram Uses ultrasound to visualize heart structure and function
Non-invasive ultrasound, similar to traditional imaging
Stress Test (Exercise ECG) Assesses heart function under physical stress (e.g., treadmill)
You'll walk or bike while being monitored
CT Coronary Angiogram / Calcium Scoring Imaging to detect blockages and measure artery calcification
Involves dye injection; uses CT scan
Advanced Imaging & Other Tests Includes MPI (nuclear stress test), coronary angiography, etc.
More detailed and may be used as follow-ups
4. Preparation Guidelines
Fasting may be required for certain blood tests (e.g., glucose, lipid panel)
Avoid caffeine or smoking before imaging tests such as CT scanning
Wear comfortable clothing, especially if undergoing a stress test
Review medication instructions—some may need to be paused or adjusted before testing
5. Benefits and Risks
Benefits:
Early detection of heart disease—often before symptoms develop
Radiologyinfo.org
Helps guide preventive treatment or interventions
Non-invasive options available for most tests
Risks:
Radiation exposure with CT scans—though low, it's considered clinically acceptable
Contrast reactions or kidney effects in imaging that use dye
Rare allergic reactions to tracers in nuclear tests
Invasive procedures, like catheter angiography, carry a slight risk of bleeding or vessel injury
6. After the Screening
Your results will explain whether your heart appears healthy or if there are areas of concern. If abnormalities are found:
You may receive recommendations on lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, quitting smoking)
Medications may be prescribed to manage cholesterol, blood pressure, or other conditions
Further diagnostics or treatments (e.g., angioplasty, stenting, bypass surgery) could be considered
Radiologyinfo.org
Even normal results can offer reassurance, though periodic reassessment may be advised for long-term monitoring.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are these tests painful?
Most are non-invasive and painless. An ECG or echo simply requires resting during a scan. Stress tests may cause shortness of breath but are closely supervised.
Is CT imaging safe?
Modern CT scanners use low radiation doses. The diagnostic benefits usually outweigh very small risks.
What happens if results are abnormal?
Not all findings indicate serious problems. Many can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes or medication. Early detection improves outcomes.
8. Tips for a Smooth Screening Experience
Arrive on time and wear comfortable, loose clothing
Be prepared to fast if instructed
Carry current medical history information, including allergies or medications
Ask your doctor any questions—understanding the process helps reduce anxiety
9. Disclaimer
For more details you can consult us for personalized guidance, interpretation of results, and appropriate next steps.




